Aerosols play a crucial role in our daily lives, often without us even realizing it. From the spray you use to freshen up your home to the tiny particles that linger in the atmosphere, understanding aerosols is essential for grasping their impact on health and the environment. Have you ever wondered how these microscopic particles influence air quality or weather patterns?
Overview of Aerosols
Aerosols consist of tiny particles or droplets suspended in the air. They play a significant role in various contexts, from household products to environmental processes. Understanding aerosols helps you grasp their effects on health and climate.
- Household Products: Many items, such as air fresheners, deodorants, and cleaning sprays contain aerosolized substances.
- Atmospheric Aerosols: Dust, smoke from wildfires, and sea spray contribute to natural aerosol formation in the atmosphere.
- Medical Applications: Inhalers deliver medication as aerosols for respiratory conditions like asthma.
- Industrial Uses: Spray paints and coatings utilize aerosols for even application on surfaces.
Each example illustrates how aerosols impact daily life. You might not notice them often, but they affect air quality and weather patterns significantly. What’s more surprising is their influence on climate change through interactions with sunlight and clouds.
Types of Aerosols
Aerosols can be classified into two main categories: natural aerosols and anthropogenic aerosols. Each type influences air quality, climate, and health in distinct ways.
Natural Aerosols
Natural aerosols occur from organic processes in the environment. They include:
- Dust: Particles lifted from deserts or dry regions comprise minerals and organic material.
- Sea Spray: Droplets generated by wave action carry salt particles into the atmosphere.
- Pollen: Plant reproductive cells released during flowering contribute to seasonal aerosol levels.
- Volcanic Ash: Eruptions release fine particles that can affect air travel and climate.
Natural aerosols significantly impact weather patterns and ecosystems. They help form clouds by providing surfaces for water vapor to condense.
Anthropogenic Aerosols
Anthropogenic aerosols are produced by human activities. They include:
- Industrial Emissions: Factories release soot, metals, and chemical compounds into the air.
- Vehicle Exhaust: Cars and trucks emit particulate matter that contributes to urban smog.
- Agricultural Practices: Plowing fields or burning crop residue introduces dust and smoke particles.
- Household Products: Aerosol sprays like deodorants or cleaners disperse chemicals into the atmosphere.
Anthropogenic aerosols play a crucial role in air pollution. Their presence can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems.
Aerosols and Climate Change
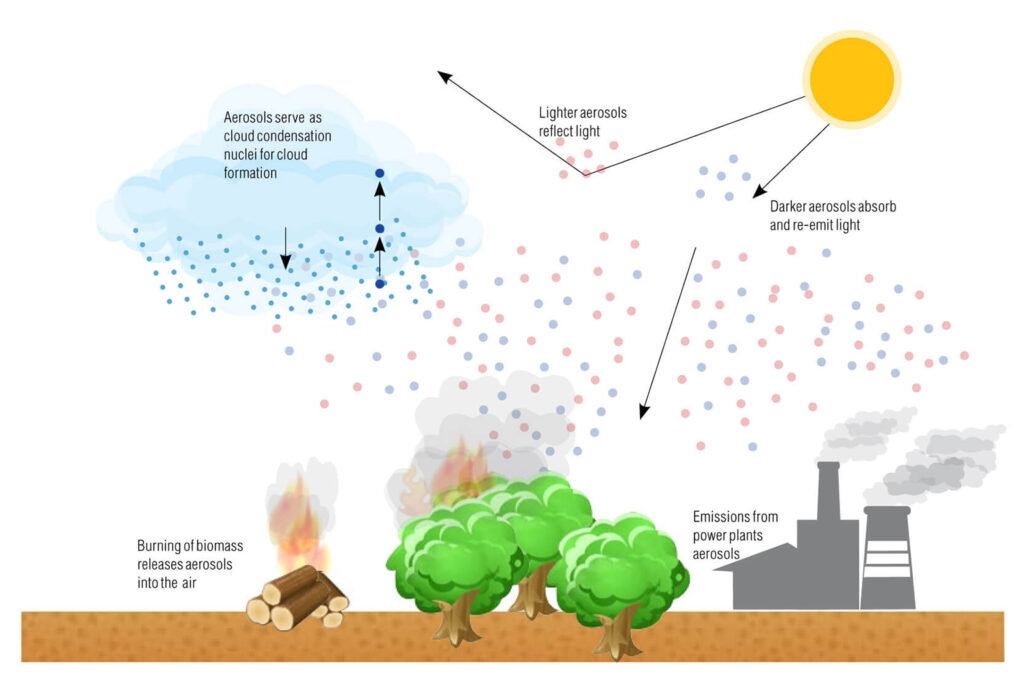
Aerosols significantly influence climate change through their interactions with solar radiation and cloud formation. Understanding these impacts is crucial for grasping the broader implications of aerosols on Earth’s climate systems.
Impact on Solar Radiation
Aerosols affect solar radiation by either absorbing or scattering sunlight. For example, <strong:black carbon, a type of aerosol produced from incomplete combustion, absorbs sunlight and warms the atmosphere. In contrast, <strong sulfates reflect sunlight back into space, leading to a cooling effect. These opposing effects can alter regional climates.
- Black Carbon: Absorbs heat; contributes to warming.
- Sulfates: Reflects light; causes cooling.
Do you see how these interactions can complicate climate models? They create feedback loops that influence temperature patterns and precipitation cycles.
Effects on Cloud Formation
Aerosols play a vital role in cloud formation by acting as nuclei for water droplets. This process affects cloud properties and lifetimes. For instance, <strong more aerosols lead to smaller droplets, resulting in clouds that persist longer but contain less rain. Consequently, this affects local weather conditions.
- Cloud Albedo Effect: More aerosols increase cloud brightness.
- Precipitation Changes: Smaller droplets reduce rainfall intensity.
Have you noticed how persistent clouds might lead to prolonged dry spells? The interaction between aerosols and clouds showcases their complex role in regulating Earth’s climate system.
Health Impacts of Aerosols
Aerosols significantly impact health, influencing both respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Understanding these effects is essential for recognizing the importance of air quality.
Respiratory Disorders
Aerosols contribute to various respiratory disorders. Exposure to fine particulate matter can lead to conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). For instance:
- Asthma attacks: Aerosolized allergens like pollen and mold trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals.
- Bronchitis: Inhalation of smoke from wildfires or industrial emissions can irritate airways, leading to bronchitis.
- Lung infections: Bacteria and viruses carried by aerosols increase the risk of respiratory infections.
These examples highlight how aerosols play a critical role in respiratory health issues.
Cardiovascular Issues
Aerosols also affect cardiovascular health. Research indicates that long-term exposure to air pollution, particularly fine particles, increases heart disease risk. Specifically:
- Heart attacks: Fine particulate matter can cause inflammation and strain on the heart.
- Stroke risk: Studies link aerosol exposure with increased chances of strokes due to blood vessel constriction.
- Hypertension: Air pollutants contribute to high blood pressure, which elevates overall cardiovascular risks.
These connections emphasize the significant impact aerosols have on heart health.
Measuring Aerosol Concentrations
Measuring aerosol concentrations involves various methods and technologies to ensure accuracy and reliability. Understanding these techniques helps assess the impact of aerosols on health and the environment.
Methods and Technologies
A range of methods exists for measuring aerosol concentrations. Common techniques include:
- Optical particle counters: These devices use light scattering to measure particle size and concentration in real-time.
- Gravimetric sampling: This method collects aerosols on filters, allowing for weight analysis after a specified time period.
- Nephelometers: These instruments measure the intensity of light scattered by particles, providing insights into aerosol properties.
- Condensation nucleus counters (CNC): CNCs detect small particles by counting droplets formed when air is supersaturated with vapor.
These technologies enable researchers to quantify aerosol levels accurately, crucial for analyzing their effects on air quality.
Challenges in Measurement
Measuring aerosol concentrations presents several challenges. One major issue lies in the variability of aerosols themselves. Since they can differ widely in size, composition, and source, standardizing measurement approaches proves difficult. Additionally:
- Environmental conditions can influence measurements significantly.
- Calibration of instruments requires precision to avoid skewed results.
- Real-time data collection often faces limitations due to equipment sensitivity.
Addressing these challenges remains essential for obtaining reliable data that informs public health policies and environmental regulations.