Adjective clauses can transform your writing from ordinary to extraordinary. Have you ever wondered how to add depth and detail to your sentences? Understanding adjective clauses examples is the key to enhancing your descriptive skills. These clauses provide essential information about a noun, making your statements clearer and more engaging.
Understanding Adjective Clauses
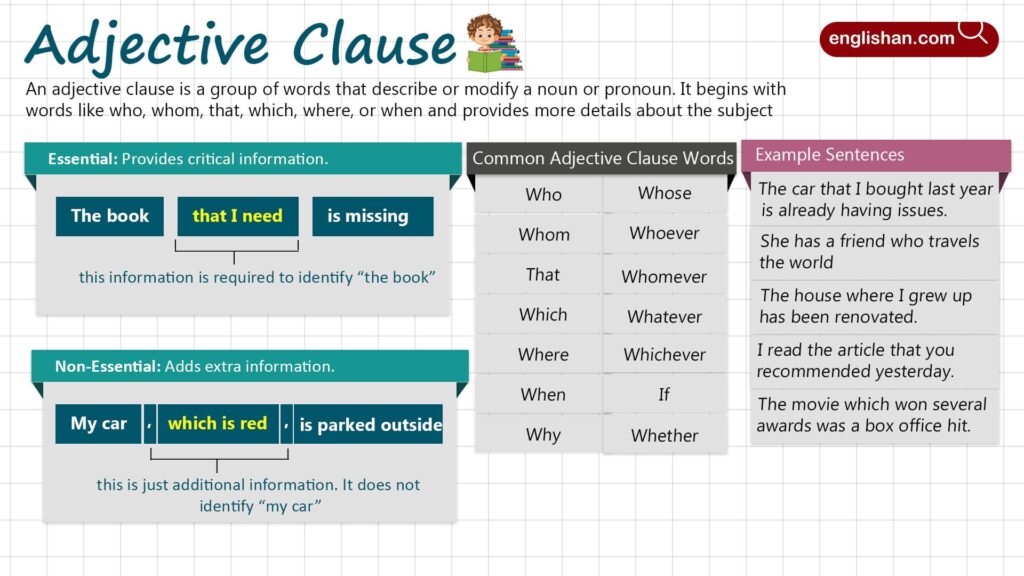
Adjective clauses add depth and detail to sentences, making your writing more engaging. They provide essential information about nouns, enhancing clarity.
Definition of Adjective Clauses
An adjective clause is a dependent clause that modifies a noun or pronoun. It usually begins with relative pronouns such as who, whom, whose, which, or that. For example:
- The book that you lent me was fascinating.
- The teacher who inspires us deserves recognition.
These clauses give readers crucial details about the nouns in your sentences.
Importance in English Grammar
Understanding adjective clauses is vital for constructing clear and informative sentences. They help you:
- Add specificity, like “The car that won the race is blue.”
- Avoid ambiguity, for instance, “The artist whose work I admire is local.”
- Create complex sentences that enhance readability and engagement.
By mastering adjective clauses, you’ll improve your descriptive skills significantly.
Types of Adjective Clauses
Adjective clauses fall into two categories: defining and non-defining. Each type serves a distinct purpose in a sentence, providing clarity and detail.
Defining Adjective Clauses
Defining adjective clauses provide essential information about the noun they modify. Without these clauses, the meaning of the sentence changes significantly. For example, consider “The car that is parked outside belongs to my neighbor.” The clause “that is parked outside” identifies which specific car you’re referring to.
Another instance is “Students who study diligently achieve better grades.” Here, “who study diligently” specifies which students are being discussed. These clauses answer questions like which one or what kind, making them crucial for clarity.
Non-defining Adjective Clauses
Non-defining adjective clauses add extra information but aren’t essential for understanding the main point. You can remove them without altering the core meaning of the sentence. For instance, “My brother, who lives in New York, is visiting this weekend.” The clause “who lives in New York” offers additional context but isn’t necessary to identify your brother.
Another example includes “The book, which was published last year, received awards.” In this case, “which was published last year” adds interesting details but isn’t vital for identifying the book. These clauses often use commas to separate from the main clause, indicating their non-essential nature.
Examples of Adjective Clauses
Adjective clauses enhance the meaning of sentences by providing additional information about nouns or pronouns. Here are some common examples that illustrate their usage.
Common Examples
- The house that you bought needs repairs.
This clause specifies which house you’re talking about, making it clear for the reader.
- The dog who barked all night kept me awake.
Here, “who barked all night” describes the specific dog, adding important detail to the sentence.
- The movie that won several awards impressed everyone.
The clause identifies which movie is being discussed, emphasizing its significance.
- My friend whose car broke down called for help.
This example shows possession and clarifies which friend is being referred to.
- The dress that she wore to the party was stunning.
In this case, the clause pinpoints which dress stands out in conversation.
Complex Sentences with Adjective Clauses
Complex sentences often contain adjective clauses that enrich their structure:
- I read a book that changed my perspective on life yesterday.
The clause adds depth by explaining what kind of book had an impact on you.
- She visited a museum where they showcased ancient artifacts last weekend.
The adjective clause helps specify not just any museum but one with particular exhibitions.
- He enjoys playing games that challenge his skills against others online.
This illustrates how certain types of games appeal specifically to him through added context in the adjective clause.
- They attended a concert whose tickets were sold out within hours last month.
By including information about ticket availability, this sentence provides insight into the event’s popularity.
Using these examples enhances your understanding of how adjective clauses function in different contexts and improves your writing clarity and engagement.
Using Adjective Clauses in Writing
Adjective clauses play a crucial role in making your writing more descriptive and engaging. They provide essential details about nouns, enhancing clarity.
Enhancing Sentences
Adjective clauses add depth to sentences by specifying or describing nouns. For instance, consider the sentence “The artist who painted that mural is famous.” Here, the clause “who painted that mural” gives you specific information about which artist is being discussed. You can also say, “The book that I borrowed from the library was a bestseller,” where “that I borrowed from the library” clarifies which book you mean. These examples show how adjective clauses turn simple statements into informative ones.