Managing your business’s finances can be a daunting task, but understanding accounts payable is crucial for maintaining healthy cash flow. Have you ever wondered how timely payments impact relationships with suppliers and overall operational efficiency? By grasping the ins and outs of accounts payable, you can streamline processes that not only save time but also enhance your company’s reputation.
In this article, we’ll explore real-world examples of effective accounts payable strategies that businesses use to optimize their financial operations. You’ll discover how implementing automated systems and best practices can lead to significant improvements in accuracy and efficiency. Get ready to dive into actionable insights that will transform the way you handle your payables, ensuring you’re always ahead of the game in today’s competitive market.
Overview of Accounts Payable
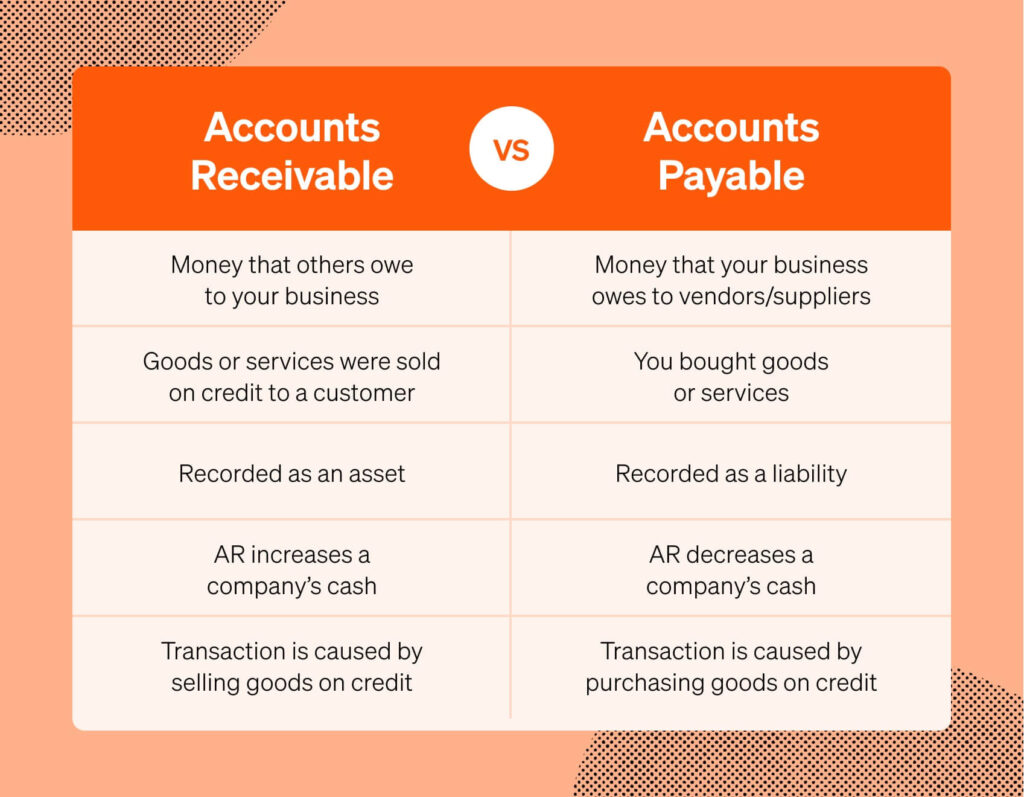
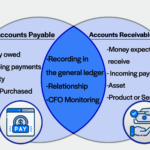
Accounts payable (AP) represents a crucial aspect of business finance management. It includes all short-term obligations that a company owes to its suppliers for goods and services received but not yet paid for. Understanding AP is vital for maintaining strong supplier relationships and ensuring operational efficiency.
Definition and Importance
Accounts payable refers to the amount a business owes its creditors for purchases made on credit. This function plays an essential role in cash flow management by tracking outgoing payments. For example, if you delay payments, suppliers may impose late fees or halt future deliveries, impacting your operations. Therefore, managing accounts payable effectively contributes to financial stability and long-term success.
How It Works
- Invoice Receipt: You receive invoices from suppliers after purchasing goods or services.
- Verification: Your team checks these invoices against purchase orders to ensure accuracy.
- Approval: Once verified, authorized personnel approve the payment.
- Payment Processing: Finally, you schedule and execute the payment based on agreed terms.
By streamlining these steps through automated systems, businesses can enhance accuracy and improve cash flow management significantly.
Key Components of Accounts Payable
Understanding the key components of accounts payable (AP) enhances your ability to manage finances effectively. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operations and maintaining supplier relationships.
Invoice Processing
Invoice processing involves several steps to ensure accuracy and timeliness. First, you receive invoices from vendors for goods or services rendered. Next, verify these invoices against purchase orders and delivery receipts to confirm correctness. After verification, obtain necessary approvals from relevant departments before processing payments. This systematic approach reduces errors and ensures timely payments, which helps maintain strong vendor relationships.
Payment Methods
Selecting appropriate payment methods impacts cash flow management significantly. Common options include checks, electronic fund transfers (EFT), credit cards, and online payment platforms like PayPal or ACH transfers. Each method has its pros and cons; for instance, EFTs typically offer quicker transactions compared to traditional checks. By evaluating your business needs, you can choose methods that optimize efficiency while minimizing costs.
Vendor Management
Effective vendor management is vital for seamless accounts payable operations. Develop strong relationships with suppliers by maintaining open lines of communication regarding payment terms and expectations. Regularly review vendor performance based on factors such as product quality, pricing, and reliability. Additionally, consider diversifying your vendor base to mitigate risks associated with relying on a single supplier. This proactive approach strengthens partnerships and supports better negotiation opportunities in future dealings.
Best Practices in Accounts Payable
Effective management of accounts payable (AP) leads to improved cash flow and stronger supplier relationships. Implementing best practices can significantly enhance your AP processes, fostering efficiency and compliance.
Automation and Technology
Automation streamlines the invoice processing cycle. By using software solutions like QuickBooks or SAP Concur, you eliminate manual entry errors. Additionally, automated workflows ensure timely approvals, reducing delays in payments. For instance, consider using e-invoicing systems that allow suppliers to submit invoices electronically. This method enhances tracking and provides a clear audit trail.
- Use cloud-based platforms for remote access.
- Implement optical character recognition (OCR) for faster data extraction.
- Integrate payment solutions with existing accounting software.
Such tools not only save time but also improve accuracy in financial reporting.
Control and Compliance
Establishing strong controls safeguards against fraud. Create a multi-step approval process where invoices require verification from multiple stakeholders. Regular audits of your AP processes help identify discrepancies early on. For example, set up monthly reviews of outstanding invoices to maintain accurate records.
- Train staff on compliance regulations relevant to your industry.
- Develop clear policies for vendor selection and payment terms.
- Utilize checklists during invoice processing to ensure all steps are followed.
By focusing on control measures, you minimize risks associated with financial mismanagement while promoting a transparent environment within your organization.
Common Challenges in Accounts Payable
Managing accounts payable presents several challenges that can impact a business’s financial health. Recognizing these issues helps you take proactive steps to mitigate them.
Delays and Errors
Delays and errors in the accounts payable process frequently occur, leading to strained supplier relationships. For instance, if invoices aren’t matched with purchase orders correctly, payment may get delayed. This not only results in late fees but also affects your credit terms. Common causes of delays include:
- Manual data entry mistakes: These often lead to inaccuracies.
- Missing approvals: Without timely approvals, payments slow down.
- Inefficient workflows: Poorly designed processes create bottlenecks.
Streamlining invoice processing through automation reduces these errors significantly.
Fraud Risks
Fraud risks pose a considerable threat within accounts payable systems. Unscrupulous employees might exploit weaknesses for personal gain. To combat this risk, implement strong internal controls and foster a culture of transparency. Key strategies include:
- Segregating duties: Ensure different individuals handle invoicing and payment approvals.
- Regular audits: Conducting audits helps identify suspicious activities early on.
- Vendor verification: Always verify new vendors before processing payments.
By prioritizing fraud prevention measures, you protect your company’s financial integrity while maintaining trust with suppliers.