Prepositions are the unsung heroes of our sentences, connecting words and adding clarity. Ever wondered how a simple word can change the meaning of a sentence? Understanding the 8 types of prepositions with examples will not only enhance your writing but also improve your communication skills.
Overview Of Prepositions
Prepositions serve as crucial elements in sentences. They establish relationships between nouns, pronouns, and other words. Understanding prepositions can significantly improve your writing clarity.
Prepositions typically indicate time, place, direction, or manner. For example:
- Time: “The meeting starts at 10 AM.”
- Place: “The book is on the table.”
- Direction: “She walked to the store.”
- Manner: “He spoke with confidence.”
Learning about different types of prepositions enhances communication skills. Familiarity with how a single preposition can change sentence meaning is vital for effective expression.
In essence, mastering prepositions leads to clearer sentences and better overall communication. You’ll notice that using the correct preposition makes your writing more precise and impactful.
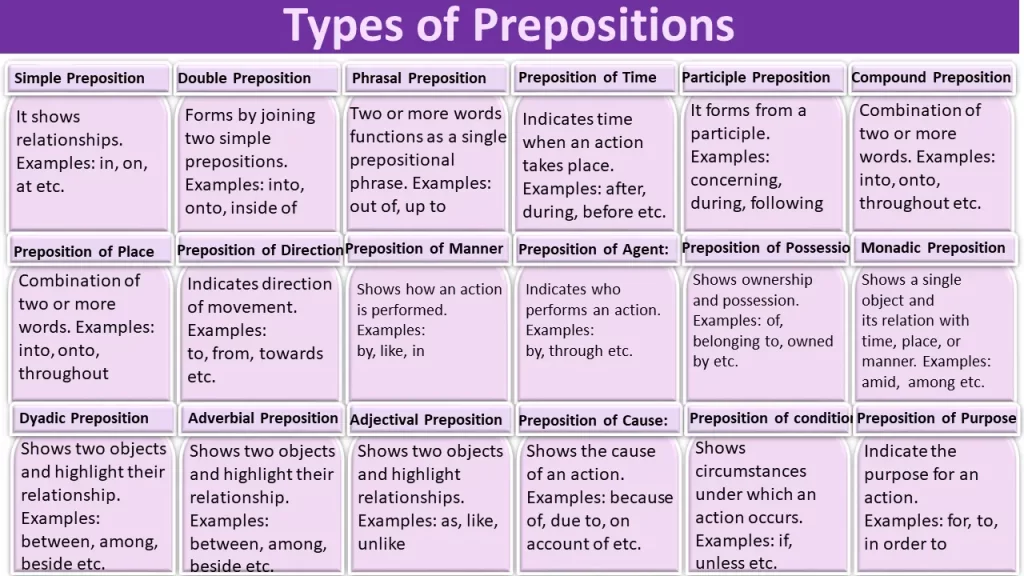
Types Of Prepositions
Prepositions play a crucial role in sentence structure. Understanding their types enhances clarity and precision in communication.
Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions consist of single words that indicate relationships between nouns and other elements. Examples include “in,” “on,” and “at.” You use them to create clear connections in sentences, such as:
- The cat is in the box.
- The book is on the shelf.
- He arrived at noon.
Compound Prepositions
Compound prepositions combine two or more words into one cohesive unit, enhancing meaning. Common examples are “according to,” “due to,” and “in front of.” They offer specific relational context, like:
- According to the report, sales increased.
- Due to the rain, the event was canceled.
- She stood in front of the mirror.
Phrasal Prepositions
Phrasal prepositions involve phrases that function similarly to simple prepositions. Examples include “out of,” “instead of,” and “as well as.” These expressions add depth to your sentences:
- He walked out of the room.
- Instead of coffee, she chose tea.
- She is talented as well as hardworking.
Prepositions Of Time
Prepositions of time specify when something occurs. Key examples are “before,” “after,” and “during.” These help you establish timelines clearly:
- We met before lunch.
- I’ll call you after work.
- They played during the summer.
Prepositions Of Place
Prepositions of place indicate where something exists or happens. Common ones include “between,” “among,” and “behind.” Use these for spatial clarity:
- The keys are between the couch cushions.
- She felt safe among friends.
- The dog is hiding behind the curtain.
Prepositions Of Direction
Prepositions of direction express movement toward a location. Examples like “to,” “toward,” and “into” guide readers on physical orientation:
- He walked to school every day.
- She moved toward her goal with determination.
- The cat jumped into the box.
Prepositions Of Manner
Prepositions of manner describe how an action occurs. Words such as “by,” “like,” and “with” illustrate methods effectively:
- He traveled by train for convenience.
- She sings like an angel at concerts
- I made it with care so it would last longer.
- He cut the paper with scissors.
- They traveled by means of a bicycle tour.
- She solved it through careful analysis.
Examples Of Each Type
Understanding different types of prepositions enhances your communication skills. Here are examples for each type:
Simple Prepositions
- In: The cat is sleeping in the box.
- On: The keys are on the counter.
- At: She arrived at noon.
Compound Prepositions
- According to: According to the report, sales increased.
- Due to: The game was canceled due to rain.
Phrasal Prepositions
- Out of: He jumped out of the pool.
- Instead of: Choose salad instead of fries.
Prepositions of Time
- Before: Finish your homework before dinner.
- After: We’ll meet again after lunch.
Prepositions of Place
- Between: The park is located between Main Street and Oak Avenue.
- Among: She found her phone among the cushions.
Prepositions of Direction
- To: They walked to the store.
- Toward: He ran <strong_toward_The finish line.
- By: Travel by train for convenience.
- With: She completed the project with great care.