The foundation of American democracy rests on the 7 principles of the Constitution. These guiding tenets not only shape our government but also protect your rights as a citizen. Have you ever wondered how these principles influence your daily life and the decisions made by those in power?
Overview of the 7 Principles of the Constitution
The seven principles of the Constitution lay the groundwork for American governance and protect individual rights. Each principle plays a vital role in maintaining democracy.
- Popular Sovereignty: This principle emphasizes that government derives its power from the consent of the governed. You can see this in action during elections when citizens choose their representatives.
- Limited Government: Limited government ensures that no individual or group holds absolute power. For instance, laws apply equally to all, including elected officials.
- Separation of Powers: This principle divides government into three branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. Each branch has distinct responsibilities which prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful.
- Checks and Balances: Checks and balances allow each branch to monitor and limit the others’ powers. For example, while Congress makes laws, the President can veto them, ensuring collaboration among branches.
- Judicial Review: Judicial review gives courts authority to interpret laws and declare them unconstitutional if necessary. You might recall landmark cases like Marbury v. Madison that established this crucial function.
- Federalism: Federalism distributes power between national and state governments, allowing both levels to operate effectively within their spheres of influence.
- Republicanism: Republicanism emphasizes a system where citizens elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf instead of direct participation in every decision-making process.
These principles collectively shape how you experience democracy daily while safeguarding your rights as a citizen.
Popular Sovereignty
Popular Sovereignty emphasizes that government derives its power from the consent of the governed. It’s a foundational principle that underscores democracy in America, ensuring citizens play a crucial role in shaping their government.
Definition and Importance
Popular sovereignty means that the authority of the government comes directly from the people. This principle is essential because it establishes a system where citizens have the right to choose their leaders and influence decisions affecting their lives. Without this concept, governance could easily become disconnected from public interests.
Examples in Government
Examples of popular sovereignty are evident in various aspects of American democracy:
- Elections: Citizens vote for representatives at local, state, and national levels. These elections reflect public choice and accountability.
- Referendums: In certain cases, voters can directly decide on specific issues or policies through referendums. This mechanism allows for direct participation in governance.
- Public Opinion Polls: Government officials often consult polls to gauge community preferences, ensuring they align with constituents’ desires.
These mechanisms illustrate how popular sovereignty functions practically within governmental frameworks.
Limited Government
Limited government ensures that no individual or group holds absolute power, protecting citizens’ rights and freedoms. This principle establishes clear boundaries for governmental authority, preventing overreach and abuse.
Constitutional Boundaries
Constitutional boundaries define the limits of government action. These boundaries are outlined in the Constitution itself, which specifies powers granted to federal and state entities. For instance:
- Enumerated Powers: The Constitution lists specific powers Congress possesses, such as regulating commerce and declaring war.
- Reserved Powers: Powers not delegated to the federal government remain with states, allowing local governance.
- Prohibitions: Certain actions are expressly prohibited to both federal and state governments, protecting individual liberties.
These examples illustrate how constitutional boundaries maintain a balance between authority and freedom.
Role of the Judicial System
The judicial system plays a critical role in enforcing limited government principles. It acts as a guardian of constitutional rights by interpreting laws and ensuring they align with constitutional provisions. Key functions include:
- Judicial Review: Courts assess whether laws violate the Constitution, removing unjust statutes from effect.
- Case Law Precedents: Court decisions establish legal precedents that guide future cases, reinforcing limitations on government power.
- Individual Rights Protection: Courts uphold citizens’ rights against governmental infringement through litigation.
Through these mechanisms, the judicial system ensures that limited government remains a fundamental aspect of American democracy.
Separation of Powers
Separation of powers prevents any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. This principle divides the government into three branches, each with distinct roles and responsibilities.
Three Branches of Government
The U.S. government consists of three branches: Legislative, Executive, and Judicial.
- Legislative Branch: Comprises Congress, which creates laws. It includes the House of Representatives and the Senate.
- Executive Branch: Enforced by the President, this branch implements laws and conducts foreign policy.
- Judicial Branch: Courts interpret laws and ensure they align with the Constitution.
Each branch operates independently but collaborates to govern effectively.
Checks and Balances
Checks and balances create a system where each branch monitors others to maintain fairness.
- The Legislative Branch can impeach officials in the Executive Branch.
- The Executive can veto legislation passed by Congress.
- The Judicial reviews actions taken by both other branches for constitutionality.
This structure promotes accountability within government operations. How often do you think these mechanisms come into play?
Federalism
Federalism distributes power between national and state governments, allowing each level to operate independently in certain areas. This balance enhances governance by ensuring local needs are met while maintaining a unified national framework.
Division of Powers
Division of Powers allocates specific responsibilities to different government levels. For instance, the federal government manages immigration and foreign affairs, while states govern education and transportation. This separation ensures that issues can be handled at the most effective level, addressing both local concerns and national interests.
State vs. Federal Authority
State vs. Federal Authority often leads to debates over jurisdiction. States possess rights under the Tenth Amendment, granting them powers not explicitly given to the federal government. Consider these examples:
- Healthcare: States can regulate health services within their boundaries.
- Education: Each state sets its own curriculum standards.
- Law Enforcement: Local law enforcement agencies enforce state laws.
These instances illustrate how federalism allows for a tailored approach based on regional needs while still adhering to overarching national laws.
Judicial Review
Judicial review empowers courts to interpret laws and assess their constitutionality. This principle ensures that no law contradicts the Constitution, safeguarding individual rights against governmental overreach.
Power of the Courts
Courts wield significant power through judicial review. They can invalidate laws or executive actions deemed unconstitutional. For example, if Congress passes a law infringing on free speech, the Supreme Court can strike it down to uphold constitutional protections. This authority reinforces the judiciary’s role as a check on legislative and executive powers.
Landmark Supreme Court Cases
Several landmark cases illustrate the impact of judicial review in American history:
- Marbury v. Madison (1803): Established judicial review, affirming that courts can nullify laws conflicting with the Constitution.
- Brown v. Board of Education (1954): Declared racial segregation in public schools unconstitutional, demonstrating how judicial review protects civil rights.
- Roe v. Wade (1973): Recognized a woman’s right to choose an abortion based on privacy rights under the Constitution.
These cases exemplify how judicial review shapes American law and society by ensuring adherence to constitutional principles.
Individual Rights
Individual rights form a crucial part of the Constitution, ensuring that every citizen enjoys specific protections and freedoms. They empower you to express yourself, practice your beliefs, and secure your personal safety from government interference.
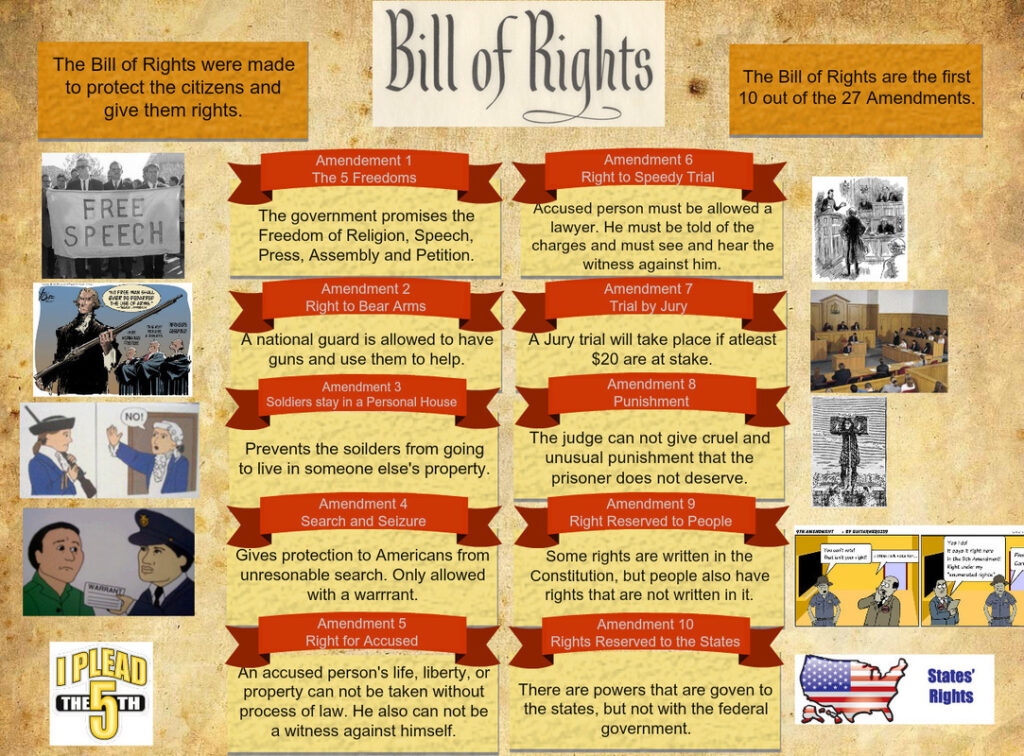
Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights encompasses the first ten amendments to the Constitution, safeguarding essential liberties. It includes important provisions such as:
- Freedom of Speech: You can express opinions without fear of government censorship.
- Right to Bear Arms: Citizens have the right to own firearms for self-defense.
- Protection Against Unreasonable Searches: Law enforcement must obtain warrants based on probable cause before searching your property.
- Due Process: Legal proceedings must be fair, giving you a chance to defend yourself in court.
These amendments illustrate how individual rights are fundamental to American democracy.
Protection of Liberties
Individual rights provide robust protection for various liberties. These include:
- Freedom of Religion: You can practice any religion or none at all without government interference.
- Right to Assemble Peacefully: Gather with others for protests or events without fear of reprisal.
- Right to Privacy: Personal information is safeguarded from unwarranted intrusion by the state.
These protections ensure that your freedoms remain intact while promoting a society where diverse perspectives thrive.