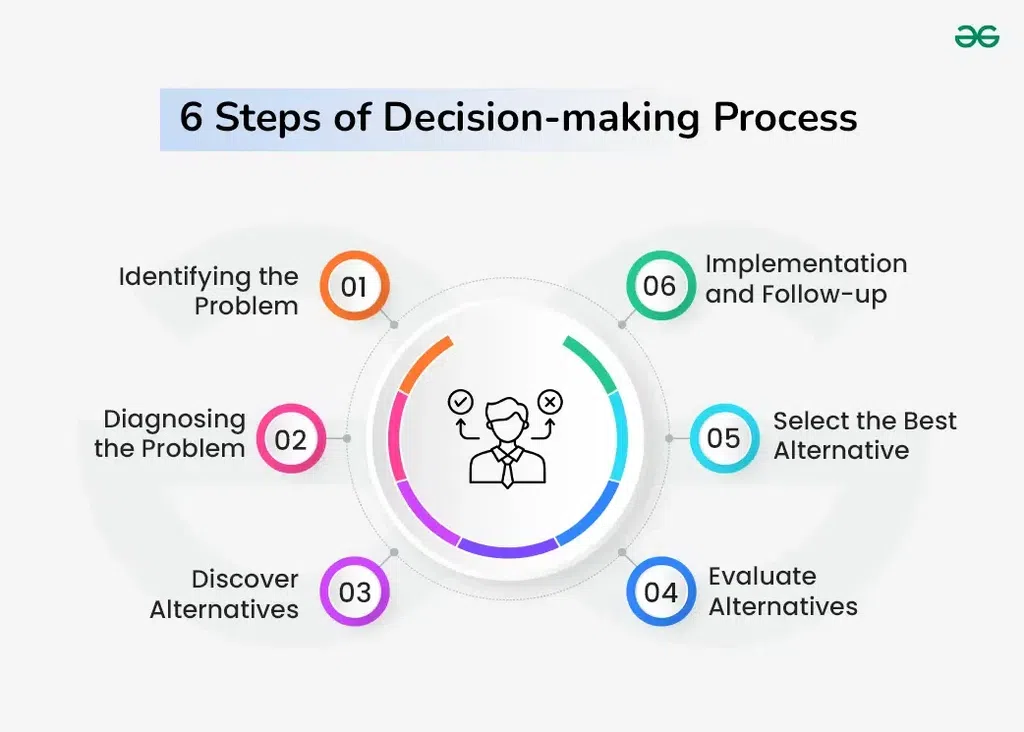
Making decisions can often feel overwhelming, but understanding the 6 steps in the decision making process can simplify it. Whether you’re choosing a career path, deciding on a major purchase, or navigating personal relationships, having a structured approach can lead to better outcomes.
So what exactly are these steps? Each one plays a crucial role in guiding you from identifying a problem to evaluating your options and making informed choices. By following this framework, you’ll not only enhance your decision-making skills but also build confidence in your ability to tackle various situations.
Overview of the Decision Making Process
The decision-making process consists of a series of steps that guide you toward making informed choices. Each step contributes to achieving clarity and confidence in your decisions. Understanding this process helps in various scenarios, like selecting a career path or choosing a new car.
- Identify the Decision Requirement: Recognizing when a choice is necessary sets the foundation for effective decision-making.
- Gather Relevant Information: Collect data from reliable sources, such as expert opinions, research studies, or personal experiences.
- Evaluate Alternatives: Assess each option based on criteria like cost, benefits, and potential outcomes.
- Make the Choice: After weighing options thoroughly, proceed with your selected alternative confidently.
- Implement the Decision: Take action to put your choice into practice and monitor its effectiveness over time.
- Review Your Decision: Reflect on the outcomes after implementation. Determine if adjustments are needed for future decisions.
Following these steps provides a structured approach that enhances both personal and professional decision-making skills. By applying this framework consistently, you’ll find it easier to navigate complex situations effectively.
Step 1: Identify the Problem
Identifying the problem is crucial in the decision-making process. You must recognize what needs addressing before you can move forward effectively.
Understanding the Challenge
Understanding the challenge requires clarity on what you’re facing. Ask yourself questions like, “What specific issue am I encountering?” or “Why does this situation matter?” For instance, if you’re struggling with low sales at your business, pinpoint whether it’s due to marketing strategies, customer engagement, or product quality. By defining these aspects clearly, you’ll gain insight into the root cause of your challenges.
Setting Objectives
Setting objectives shapes your approach to solving the problem. Establish clear goals that outline what success looks like. For example:
- Increase sales by 20% within six months
- Improve customer satisfaction ratings from 75% to 90%
By setting measurable and realistic objectives, you create a roadmap for your next steps. This not only keeps you focused but also provides motivation as you progress toward solutions.
Step 2: Gather Information
Gathering relevant information is essential for making informed decisions. This step involves collecting data from various sources to understand the situation better and identify potential solutions. Effective information gathering helps you weigh your options and reduces uncertainty.
Sources of Information
Utilize diverse sources to gather comprehensive information. Consider these:
- Books: Look for publications that provide insights into your specific topic.
- Articles: Research journals or online articles can offer current trends and findings.
- Surveys: Conduct surveys to gather opinions directly from individuals affected by the decision.
- Experts: Consult with professionals who have experience in the area related to your decision.
Using multiple sources enriches your understanding, enabling you to make a more balanced choice.
Analyzing Data
After collecting data, analyzing it becomes crucial. Focus on these key points when examining the information:
- Identify Patterns: Look for trends or recurring themes in the data that may influence your decision.
- Compare Options: Evaluate how different pieces of information align with each alternative you’re considering.
- Assess Reliability: Determine if the sources are credible and trustworthy; prioritize data from reputable organizations or studies.
Analyzing data thoroughly ensures that you make decisions based on solid evidence, thus fostering confidence in your chosen path forward.
Step 3: Identify Alternatives
Identifying alternatives is a crucial step in the decision-making process. It involves exploring various options that address the problem you’ve defined. This stage opens up possibilities and helps ensure you’re not settling for the first solution that comes to mind.
Brainstorming Options
Brainstorming options encourages creativity and broad thinking. To generate alternatives effectively, consider using these techniques:
- List out ideas: Jot down every possible option without filtering them initially.
- Group discussions: Engage with team members or stakeholders to gather diverse perspectives.
- Mind mapping: Visualize connections between different ideas to uncover new paths.
This process can lead you to discover innovative solutions that might not be apparent at first glance.
Evaluating Feasibility
Evaluating feasibility narrows down your brainstormed options. You assess each alternative based on specific criteria:
- Cost considerations: Analyze the financial implications of each option.
- Time requirements: Determine how long it takes to implement each alternative.
- Resource availability: Ensure necessary resources are accessible for execution.
By prioritizing feasible alternatives, you enhance your chances of selecting a viable solution that aligns with your objectives.
Step 4: Weigh Evidence
Weighing evidence is crucial in the decision-making process. This step involves evaluating the information collected and assessing its relevance to your situation.
Pros and Cons
When weighing options, listing Pros and Cons helps clarify potential benefits and drawbacks of each alternative. For instance:
Option A:
- Pros: Low cost, quick implementation
- Cons: Limited impact, requires ongoing maintenance
Option B:
- Pros: High effectiveness, long-term benefits
- Cons: Higher initial investment, longer timeline
This method enhances clarity by visually presenting each choice’s strengths and weaknesses.
Impact Assessment
Conducting an Impact Assessment ensures you understand how each option affects stakeholders. Identify key factors such as:
- Financial implications
- Time constraints
- Human resources required
Evaluate how these elements align with your objectives. For example, if a decision significantly impacts team morale or customer satisfaction, prioritize that factor during your assessment. Focus on outcomes that resonate with your goals for informed choices moving forward.
Step 5: Choose Among Alternatives
Choosing among alternatives involves selecting the best option from the evaluated possibilities. This step demands careful consideration to ensure that the choice aligns with your objectives and values.
Making the Final Decision
Making the final decision requires clarity on which alternative best meets your established criteria. You can create a decision matrix, listing options alongside relevant factors like cost, effectiveness, and time commitment. For instance, if you’re deciding between two vendors for office supplies, compare their pricing structures and delivery times side by side. Ultimately, choose the vendor that offers value without compromising quality.
Involving Stakeholders
Involving stakeholders enhances decision-making accuracy and acceptance. Engaging team members or key individuals in discussions encourages diverse perspectives. For example, if you’re launching a new product, gather input from marketing, sales, and customer service teams to identify potential challenges early on. Their insights can uncover considerations you might overlook alone. Make sure to communicate transparently throughout this process to build trust and support among all parties involved.
Step 6: Implement the Decision
Implementing the decision marks a crucial phase in the decision-making process. This step involves putting your chosen option into action and ensuring that all necessary resources are aligned.
Action Plan Development
Creating a detailed action plan is essential for effective implementation. An action plan outlines specific steps required to execute the decision, assigns responsibilities, and sets deadlines. For instance, if you decide to launch a new marketing campaign, your action plan might include:
- Defining target audience by conducting surveys.
- Setting budget limits based on resource availability.
- Assigning tasks to team members with clear deadlines.
Clearly defined roles enhance accountability, making it easier to track progress and manage expectations throughout the implementation phase.
Monitoring Outcomes
Monitoring outcomes ensures that your decision leads to desired results. Establishing metrics prior to execution helps gauge success effectively. For example, if you implemented changes in customer service protocols, consider tracking:
- Customer satisfaction scores, collected through feedback forms.
- Response times, measured against established benchmarks.
Regularly reviewing these metrics allows for timely adjustments, ensuring you’re on course toward achieving set objectives while adapting strategies as needed.