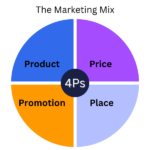
In today’s competitive marketplace, understanding the 4 P’s of marketing can set you apart from the crowd. Have you ever wondered how successful brands consistently attract and retain customers? The secret often lies in mastering these four essential elements: product, price, place, and promotion.
Overview of the 4 P’s of Marketing
The 4 P’s of marketing consist of product, price, place, and promotion. Each element plays a crucial role in shaping a brand’s overall strategy.
Product
A product refers to the goods or services offered by a business. For instance, Apple’s iPhone exemplifies innovation and quality in electronics. It meets customer needs through features like high-quality cameras and user-friendly interfaces.
Price
Price involves determining how much to charge for your product. For example, luxury brands like Rolex set high prices to create an image of exclusivity. In contrast, discount retailers like Walmart focus on competitive pricing to attract budget-conscious consumers.
Place
Place denotes where and how a product is distributed. Consider Coca-Cola; it ensures availability through various channels—grocery stores, restaurants, and vending machines worldwide. This widespread distribution makes it convenient for consumers to access their favorite beverages.
Promotion
Promotion encompasses all marketing communications aimed at informing potential customers about products. A successful campaign might include social media ads from Nike that resonate with athletes’ lifestyles. Promotions can also involve sales events or influencer partnerships that boost brand visibility.
Understanding these four components helps you craft effective marketing strategies tailored to your target audience’s preferences.
Product
Understanding your product is essential in marketing. It encompasses the goods or services you offer and their unique features that meet customer needs.
Defining Your Product
Defining your product involves identifying its core attributes and benefits. For instance, Apple’s iPhone emphasizes innovation with features like facial recognition and high-quality cameras. Alternatively, Tesla’s electric vehicles highlight environmental sustainability while offering cutting-edge technology. Think about how your product stands out in the market. Is it superior quality? Unique design? These factors can influence consumer decisions significantly.
Product Life Cycle
The product life cycle outlines the stages every product goes through: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
- Introduction: Products like virtual reality headsets are still gaining traction.
- Growth: Fitness trackers gained popularity as health awareness increased.
- Maturity: Smartphones now face fierce competition but continue to sell well.
- Decline: Traditional cameras experience a downturn due to smartphone advancements.
Recognizing where your product is within this cycle helps tailor marketing strategies effectively. Adjusting promotion efforts or innovating based on these stages can enhance longevity in the market.
Price
Price plays a crucial role in your marketing strategy. It represents the value you place on your product or service and can significantly influence customer perception. Setting the right price involves balancing profitability with consumer expectations, so it’s essential to consider various pricing strategies.
Pricing Strategies
Effective pricing strategies include:
- Cost-plus pricing: Add a markup to the cost of goods sold. For example, if a product costs $50 to produce, you might sell it for $75.
- Competitive pricing: Set prices based on competitors’ rates. If similar products are priced at $100, you could choose to price yours slightly lower at $95.
- Value-based pricing: Focus on perceived value rather than just costs. Luxury brands like Chanel use this method by charging high prices because customers associate them with prestige.
- Dynamic pricing: Adjust prices based on demand and market conditions. Airlines often utilize this by changing ticket prices according to availability and timing.
The Impact of Price on Sales
Price directly affects sales volume and brand positioning. A low price can attract budget-conscious consumers but may also devalue your brand in their eyes. Conversely, a high price can suggest quality but might deter some potential buyers.
Consider these factors when evaluating how price impacts sales:
- Consumer behavior: Are customers willing to pay more for premium features?
- Market trends: Is there an increase in demand for eco-friendly products that justify higher prices?
- Sales goals: Do you aim for quick turnover or long-term customer loyalty?
Understanding how these elements interact helps you align your pricing strategy with overall business objectives while meeting customer needs effectively.
Place
Place refers to the distribution channels for a product. It’s essential to ensure your product reaches customers effectively. Consider how Coca-Cola achieves widespread availability in grocery stores, restaurants, and vending machines. This strategy enhances brand visibility and accessibility.
Distribution Channels
Distribution channels determine how products reach consumers. Examples include:
- Direct sales: Companies like Dell sell directly through their websites.
- Retail partnerships: Brands such as Nike partner with sporting goods stores.
- E-commerce platforms: Amazon serves as a major channel for countless brands.
Each channel impacts customer experience and can influence purchasing decisions.
Location Strategy
Location strategy involves choosing where to sell your products. Think about Starbucks; its locations are often in high foot traffic areas, making it convenient for customers. Additionally, a business focusing on local markets may benefit from understanding community preferences, tailoring offerings accordingly.
Effective placement strategies enhance accessibility and convenience while supporting overall marketing goals.
Promotion
Promotion includes the strategies and tactics used to communicate with potential customers. It aims to inform, persuade, and remind consumers about products or services. Effective promotion can significantly influence brand awareness and customer engagement.
Advertising Techniques
Advertising techniques vary widely but share a common goal: reaching the right audience effectively. Some notable methods include:
- Television commercials: These capture visual attention and create memorable impressions through storytelling.
- Print advertising: Magazines or newspapers are ideal for targeting specific demographics.
- Billboards: Strategic locations increase visibility in high-traffic areas.
- Radio ads: These use sound to evoke emotion quickly and reach audiences during commutes.
Each technique has its strengths depending on the target market’s preferences.
Digital Marketing Strategies
Digital marketing strategies leverage online platforms to connect with consumers. Key approaches include:
- Social media marketing: Engaging users on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter fosters community building.
- Email campaigns: Personalized messages directly reach customers’ inboxes, promoting special offers or new products.
- Search engine optimization (SEO): Enhancing website visibility ensures your content ranks higher in search results, attracting more visitors.
- Content marketing: Providing valuable information establishes authority and builds trust among potential customers.
These strategies allow brands to adapt their messaging based on real-time feedback from their audience.