Resource markets play a crucial role in our economy, but do you know how they function? Understanding these markets can give you valuable insights into the dynamics of supply and demand. In this article, we’ll explore three compelling examples of resource markets that illustrate their importance and impact on various sectors.
Overview of Resource Markets
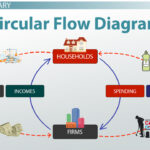
Resource markets play a vital role in the economy by facilitating the exchange of raw materials and services. Understanding these markets helps you grasp how supply and demand dynamics influence various sectors.
Definition of Resource Markets
Resource markets are platforms where resources, such as natural resources, labor, and capital, are bought and sold. These markets can be physical locations or virtual spaces. In essence, they connect buyers who need resources with sellers who provide them. For instance, when companies seek timber for construction projects, they engage in a resource market focused on forestry products.
Importance of Resource Markets
Resource markets significantly impact economic stability and growth. They ensure that essential materials reach industries efficiently. By balancing supply with demand, these markets contribute to price stabilization. When resource prices fluctuate due to scarcity or excess production, it affects not just suppliers but also consumers directly.
Key factors illustrating their importance include:
- Job Creation: Resource extraction often generates employment opportunities.
- Economic Growth: Availability of resources fuels industrial expansion.
- Innovation: Efficient resource allocation encourages technological advancements.
Ultimately, understanding resource markets equips you to better navigate both local and global economies.
Example 1: Agriculture Markets
Agriculture markets play a crucial role in the economy by facilitating the trade of agricultural commodities. These markets connect farmers with buyers, ensuring that food and raw materials reach consumers efficiently.
Overview of Agricultural Commodities
Agricultural commodities include products like grains, fruits, vegetables, and livestock. Some key examples are:
- Wheat: A staple grain used for bread and other foods.
- Corn: Utilized for animal feed and biofuels.
- Soybeans: Important for oil production and protein sources.
Understanding these commodities helps you appreciate their impact on food security and pricing.
Market Dynamics in Agriculture
Market dynamics in agriculture involve supply and demand fluctuations influenced by factors such as weather conditions, consumer preferences, and global trade policies. For instance:
- Supply shocks can result from droughts or floods affecting crop yields.
- Demand shifts may occur due to changing dietary trends or population growth.
Monitoring these dynamics is essential for farmers and investors alike. By staying informed about the market conditions, you can make better decisions regarding production and investment strategies.
Example 2: Energy Markets
Energy markets play a crucial role in the economy, facilitating the trade of various energy resources. Understanding these markets helps you grasp how energy influences everyday life and global activities.
Types of Energy Resources
Energy resources encompass several categories, each with distinct characteristics:
- Fossil Fuels: Includes coal, oil, and natural gas; these remain primary sources for electricity generation and transportation.
- Renewable Energy: Comprises solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy; these options are gaining popularity due to their sustainability.
- Nuclear Energy: Generates power through nuclear reactions; it offers a low carbon footprint but raises safety concerns.
Each type contributes differently to overall energy supply and demand dynamics.
Role of Energy Markets in the Economy
Energy markets influence economic stability significantly. They determine pricing structures that affect everything from household bills to industrial costs.
Moreover, fluctuations in energy prices can impact inflation rates and GDP growth. For instance:
- When oil prices rise sharply, transportation costs increase.
- Higher transportation costs often lead to increased consumer goods prices.
Furthermore, shifts toward renewable sources create new job opportunities while fostering innovation within green technologies. Engaging with these markets allows you to stay informed about trends impacting your finances and business operations.
Example 3: Labor Markets
Labor markets represent a vital segment of resource markets, where employers seek workers and individuals look for jobs. They serve as platforms that facilitate the exchange of labor for wages, impacting economic performance significantly.
Characteristics of Labor Markets
Labor markets exhibit distinct characteristics that set them apart from other resource markets.
- Diversity of Jobs: Various job types exist, from skilled trades to unskilled positions.
- Wage Determination: Wages fluctuate based on demand and supply for specific skills.
- Employment Types: Employment can be full-time, part-time, temporary, or freelance.
- Regulations and Policies: Government policies influence labor conditions through minimum wage laws and labor rights.
These factors shape how labor is valued in the economy. Understanding these characteristics helps you navigate job opportunities effectively.
Impact on Economic Growth
Labor markets drive economic growth by creating job opportunities and fostering innovation.
- Increased Productivity: When more individuals participate in the workforce, overall productivity rises.
- Consumer Spending: Higher employment levels lead to increased disposable income, boosting consumer spending.
- Skill Development: Investment in employee training enhances skills within the workforce.
By connecting workers with employers efficiently, labor markets contribute directly to economic stability and prosperity. Engaging with these markets allows you to recognize trends that can affect your career path or business decisions.