Have you ever wondered how certain phrases can carry so much meaning in a single sentence? Noun clauses play a crucial role in enriching our language, allowing us to express complex ideas seamlessly. These versatile structures function like nouns, making them essential for clear communication.
Overview of Noun Clauses
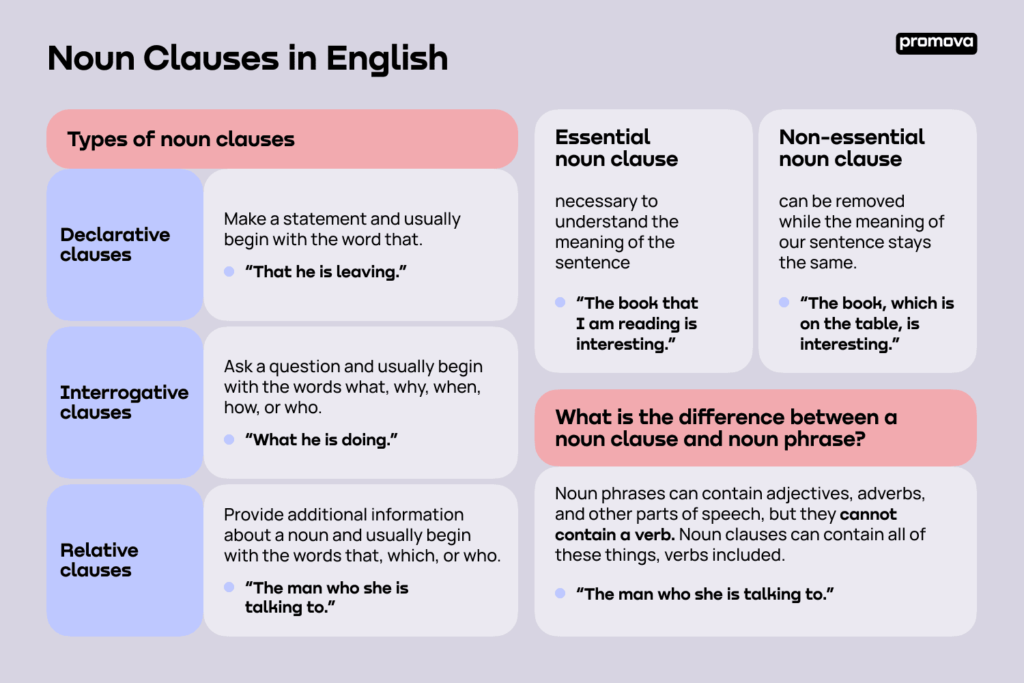
Noun clauses play a crucial role in English, allowing you to express complex thoughts effectively. They function similarly to nouns and can act as subjects or objects within sentences.
Definition of Noun Clauses
A noun clause is a group of words that contains a subject and a verb but functions as a single noun. For example, in the sentence “What you said surprised me,” the entire phrase “What you said” acts as the subject. Recognizing these clauses enhances your understanding of sentence structure.
Importance in English Grammar
Noun clauses are essential for conveying detailed information succinctly. They help clarify meaning by combining ideas into one cohesive unit. Consider these points:
- Clarity: Using noun clauses reduces ambiguity.
- Complexity: They allow for more intricate expressions without overly complicated structures.
- Variety: Incorporating them diversifies your writing style.
Incorporating noun clauses enriches both written and spoken communication, making it clearer and more engaging.
10 Examples of Noun Clauses
Noun clauses serve as essential components in sentences, acting as subjects or objects. Here are ten examples to illustrate their usage.
Example 1: What She Said
What she said surprised everyone at the meeting. This noun clause functions as the subject in this sentence, emphasizing the unexpected nature of her statement.
Example 2: Whether He Will Come
Whether he will come remains uncertain. Here, the noun clause acts as the subject, highlighting uncertainty about his attendance.
Example 3: That He Finished Early
That he finished early impressed the manager. In this case, the noun clause serves as an object, showcasing its effectiveness in conveying information.
Example 4: How They Are Feeling
How they are feeling matters a lot to you. This noun clause operates as a subject that draws attention to emotional states and their significance.
Example 5: Why She Left
Why she left is still unclear. The noun clause here acts as a subject while raising questions about her departure’s reasons.
Example 6: That You Are Here
That you are here makes me happy. In this example, the noun clause serves as an object that conveys positive feelings regarding your presence.
Example 7: What He Wants
What he wants needs more discussion. This noun clause functions as a subject and points out that further conversation is necessary for clarity.
Example 8: If She Agrees
If she agrees, we can proceed with our plans. This conditional structure allows for flexibility while indicating reliance on her decision through a noun clause acting as part of the larger context.
Example 9: Where They Went
Where they went remains a mystery to us all. The noun clause acts here as a subject that creates intrigue around their destination.
Example 10: When It Will Happen
When it will happen, nobody knows yet. This final example illustrates how the noun clause serves to express uncertainty regarding timing within discussions or plans.
Usage of Noun Clauses in Sentences
Noun clauses enhance sentence structure by acting as subjects or objects. Understanding their roles makes your writing clearer and more effective.
Noun Clauses as Subjects
Noun clauses can serve as subjects in sentences. They perform the action or are being described. For example, in the sentence “What you decide affects your future,” the clause “What you decide” serves as the subject. Here are a few more examples:
- Whether he passes the exam is uncertain.
- That she won the award surprised everyone.
These noun clauses introduce essential information right from the start.
Noun Clauses as Objects
Noun clauses function effectively as objects within sentences. They receive the action of a verb. For instance, in “I believe that honesty is crucial,” the clause “that honesty is crucial” acts as an object of belief. Consider these additional examples:
- I know what you want for your birthday.
- The teacher asked if we understood the lesson.
These noun clauses add depth to your ideas by providing specific details about actions or thoughts.
Common Mistakes with Noun Clauses
Noun clauses can enhance clarity in communication, but common mistakes often arise during their use. Recognizing these errors helps you utilize noun clauses effectively.
Incorrect Usage
Many people misuse noun clauses by confusing them with other clause types. For example, using a noun clause as if it were an adjective or adverb leads to confusion. A sentence like “The reason why he left is unclear” may seem correct, but it’s better phrased as “The reason he left is unclear.”
Another mistake involves omitting necessary conjunctions. For instance, saying “I wonder you will join us” lacks the required conjunction “if,” making it incorrect. The proper form would be “I wonder if you will join us.”
Tips for Avoiding Errors
To avoid mistakes with noun clauses, consider these tips:
- Identify the role: Determine whether the noun clause acts as a subject or an object.
- Use appropriate conjunctions: Ensure that you’re using words like “that,” “whether,” or “if” correctly.
- Simplify when possible: Rephrase complex sentences to make the use of noun clauses clearer.
- Practice regularly: Regularly writing and reviewing your sentences can strengthen your understanding of noun clauses.
By following these guidelines, you can minimize errors and improve your writing skills significantly.