Imagine holding the power of a computer in your pocket. The Android operating system makes this possible, powering billions of devices worldwide. But did you know there are various versions and adaptations of Android that cater to different needs?
Overview of Android Operating System
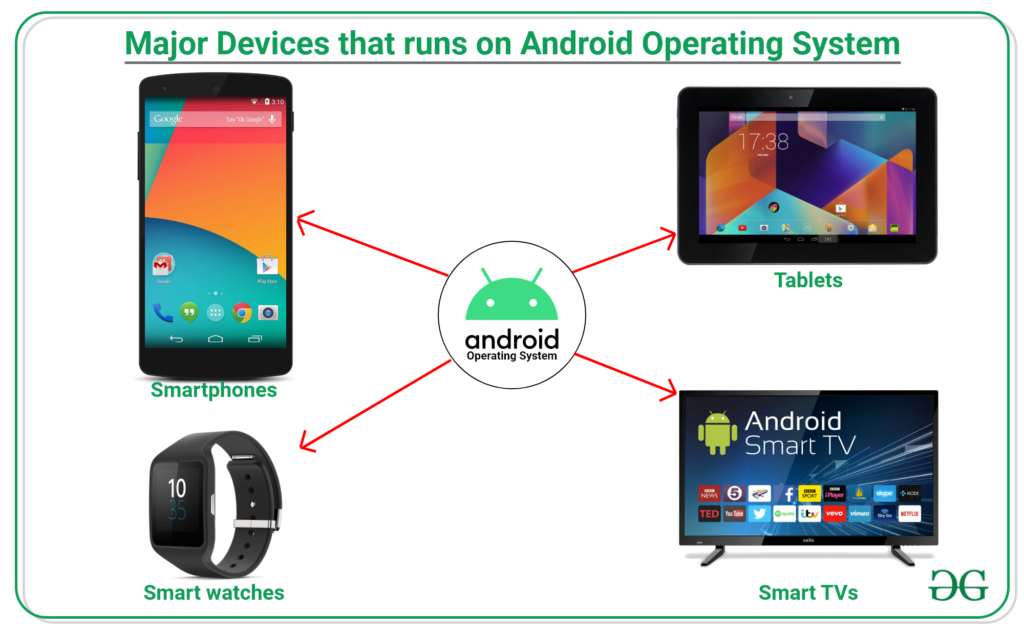
The Android operating system powers billions of devices around the world. It’s known for its flexibility and customization options. Different versions cater to various needs, from smartphones to smart TVs.
Android’s open-source nature allows developers to modify and enhance its functionalities. This encourages innovation and a wide range of applications. You can find Android in many devices, including:
- Smartphones: Most popular mobile devices run on Android, offering numerous apps.
- Tablets: These larger devices provide a similar experience as smartphones but with added screen space.
- Wearables: Smartwatches often use Wear OS, an adaptation of Android designed for wearable technology.
- Televisions: Smart TVs utilize Android TV for streaming services and apps.
- Automobiles: Android Auto integrates with car systems for navigation and entertainment.
The versatility of the Android operating system makes it suitable for various industries. From healthcare to education, businesses leverage its capabilities to meet specific demands.
Example 1: Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich
Android 4.0, known as Ice Cream Sandwich, marked a significant evolution in the Android operating system. Released in October 2011, it unified the tablet and smartphone versions of Android into one platform.
Key Features
Ice Cream Sandwich introduced several Key Features that enhanced user experience:
- Holo interface: A new visual style emphasizing clean lines and modern aesthetics.
- Face Unlock: A pioneering feature allowing users to unlock their devices using facial recognition.
- Improved multitasking: Users could easily switch between apps with a redesigned task manager.
- Enhanced notifications: Notifications became more interactive, allowing direct responses without opening apps.
These features significantly improved usability and set the standard for future updates.
Legacy Impact
The legacy of Ice Cream Sandwich is evident in its lasting influence on subsequent Android versions. Many concepts established here remain integral today:
- The Holo design language paved the way for material design principles seen in later releases.
- Face Unlock inspired advancements in biometric security across devices.
- Improved multitasking remains a core aspect of the Android experience.
Ice Cream Sandwich not only refined existing functionalities but also laid down foundational elements that continue shaping modern Android systems.
Example 2: Android 5.0 Lollipop
Android 5.0 Lollipop, released in November 2014, introduced a vibrant design and significant enhancements to user experience. This version emphasized fluidity and responsiveness across devices, making it a pivotal update in the Android ecosystem.
Key Features
- Material Design: Introduced a bold visual language that emphasized depth and motion. It made apps more intuitive with animations and transitions.
- Improved Notifications: Offered actionable notifications directly on the lock screen, allowing users to respond without unlocking their devices.
- Enhanced Battery Life: Included Project Volta, optimizing battery performance with features like Battery Saver mode for extended usage.
- Multi-user Support: Allowed multiple accounts on tablets, providing personalized experiences for each user.
- ART Runtime: Replaced Dalvik as the default runtime environment, improving app performance and reducing lag.
Legacy Impact
Android 5.0 Lollipop set new standards for UI/UX across mobile platforms. Its Material Design principles influenced countless applications and operating systems that followed. Many users still appreciate its focus on simplicity combined with functionality. Furthermore, the improvements in battery management paved the way for future advancements in energy efficiency within smartphones. The legacy of this version remains evident today as developers continue to build upon its foundational elements.
Example 3: Android 6.0 Marshmallow
Android 6.0 Marshmallow, released in October 2015, introduced several significant features that enhanced user experience and device performance. This version built on the foundation laid by its predecessors while addressing key areas like battery optimization and app permissions.
Key Features
- Doze Mode: This feature conserves battery life by reducing background activity when the device is not in use. It helps prolong battery duration significantly.
- App Permissions: You now control which permissions apps can access on a per-use basis. This increases privacy and security for users.
- Google Now on Tap: This functionality allows you to access contextual information simply by pressing the home button. It enhances search capabilities directly from any screen.
- Fingerprint Support: <strong.Android 6.0 added native fingerprint recognition support, simplifying authentication processes. It enables secure payments and quick unlocks.
- Improved Notifications: <strong.Notifications became more actionable, allowing direct responses without opening apps. This streamlines multitasking.
Legacy Impact
Android 6.0 Marshmallow left a lasting legacy on mobile operating systems. Its improvements in battery management set a new standard for future versions of Android. Additionally, the introduction of granular app permissions paved the way for increased user control over personal data, influencing how subsequent operating systems approach privacy settings. Overall, Marshmallow’s enhancements reinforced Android’s reputation as a flexible platform that prioritizes user needs while fostering innovation across devices.
Example 4: Android 7.0 Nougat
Android 7.0 Nougat, released in August 2016, brought several enhancements that improved user experience and performance across devices. This version focused on multitasking and customization, making it a significant update within the Android ecosystem.
Key Features
Android 7.0 Nougat introduced notable features:
- Split-Screen Mode: You could run two apps simultaneously on the screen.
- Improved Notifications: Notifications became more interactive with quick replies without opening apps.
- Doze on the Go: The battery-saving feature was enhanced to work during device movement.
- Customizable Quick Settings: You could customize the Quick Settings menu for easier access.
- Data Saver Mode: This allowed you to restrict background data usage for specific apps.
These features made day-to-day tasks more efficient and enjoyable.
Legacy Impact
The legacy of Android 7.0 Nougat is evident in its influence on future versions. Its emphasis on multitasking paved the way for subsequent advancements in app management and user interface design. Moreover, it set new standards for notifications that many smartphone manufacturers adopted in their skins. Consequently, developers used these features as a foundation to build even more complex applications, enhancing overall functionality within the Android ecosystem.
Example 5: Android 8.0 Oreo
Android 8.0 Oreo, released in August 2017, introduced several enhancements aimed at improving performance and user experience. This version focused on speed and efficiency, making it a significant upgrade over previous iterations.
Key Features
Android 8.0 Oreo brought important features that changed how you interact with your device:
- Picture-in-Picture Mode: You can now watch videos while navigating other apps.
- Notification Dots: Small dots appear on app icons to indicate unread notifications.
- Auto-fill Framework: This feature streamlines the login process by automatically filling in credentials.
- Improved Battery Management: Background limits help conserve battery life without sacrificing performance.
- Adaptive Icons: Icons adapt to different shapes for a more uniform look across devices.
These features enhanced usability, streamlined tasks, and improved overall device management.
Legacy Impact
The legacy of Android 8.0 Oreo is evident in its influence on subsequent versions. It set new benchmarks for multitasking and notification management. Other operating systems took cues from its design elements and functionality improvements. Moreover, the introduction of the auto-fill framework paved the way for greater security measures in managing personal data across apps.
By focusing on performance enhancements and user-friendly features, Android 8.0 Oreo contributed significantly to shaping modern Android experiences.
Example 6: Android 9.0 Pie
Android 9.0 Pie, released in August 2018, introduced several enhancements aimed at improving user experience and performance. This version focused on intuitive navigation and smarter functionalities.
Key Features
- Adaptive Battery: This feature learns your app usage patterns to optimize battery life. It prioritizes power for frequently used apps while limiting resources for those you use less often.
- Gesture Navigation: Gesture-based controls replaced traditional buttons. Users can now navigate their devices using simple swipes, making interactions smoother.
- Digital Wellbeing: This suite promotes healthy device usage habits. It includes features like App Timers and Wind Down mode to help users manage screen time effectively.
- Improved Notifications: Notifications became more actionable. Users can quickly respond to messages directly from the notification shade without needing to open apps.
Legacy Impact
Android 9.0 Pie set a foundation for future Android versions with its emphasis on user-centric design. The introduction of gesture navigation influenced subsequent operating systems by encouraging manufacturers to adopt similar approaches. Additionally, Digital Wellbeing initiatives paved the way for incorporating health-focused features into technology, reflecting growing concerns about device dependency and screen time management across various platforms.
Example 7: Android 10
Android 10, released in September 2019, introduced several significant features aimed at enhancing user experience. This version marked a shift as Google moved away from dessert-themed names to a more straightforward numbering system.
Key Features
Android 10 brought several key features that improved usability and performance:
- Dark Theme: Provides users with a sleek interface that reduces eye strain and saves battery life on OLED displays.
- Gesture Navigation: Offers an intuitive way to navigate your device without traditional buttons, allowing for smoother interactions.
- Privacy Controls: Introduces enhanced privacy settings, giving you more control over app permissions and data sharing.
- Focus Mode: Helps minimize distractions by allowing you to pause apps temporarily.
- Smart Replies: Uses machine learning to suggest responses in messaging apps, making conversations faster.
These features reflect Google’s focus on user-centric design and responsiveness to feedback.
Legacy Impact
The legacy of Android 10 lies in its foundational changes for future versions. Enhanced privacy controls set new standards for security across devices. The introduction of gesture navigation influenced how manufacturers designed their interfaces later on. Furthermore, the emphasis on digital wellbeing resonated with increasing concerns about screen time among users.
With these advancements, Android 10 paved the way for subsequent updates while maintaining Android’s reputation as a versatile operating system adaptable to evolving user needs.
Example 8: Android 11
Android 11, released in September 2025, introduced several features aimed at enhancing user experience and privacy. This version focused on communication, control, and security improvements across devices.
Key Features
Android 11 brought strong enhancements that redefined how you interact with your device:
- Conversations: Notifications for messaging apps are prioritized, making it easier to keep up with chats.
- Bubbles: You can use chat bubbles for quick access to conversations while multitasking.
- Screen Recording: Built-in screen recording allows you to capture your screen without third-party apps.
- Privacy Controls: More granular permissions give you better control over app access to sensitive data.
- Media Controls: A revamped media player centralizes audio management from notifications.
These features significantly improved usability and catered to modern communication needs.
Legacy Impact
The impact of Android 11 extends beyond its release. It established a new standard for user-friendly interactions. The focus on privacy controls influenced future versions, encouraging developers to prioritize security in their applications. Furthermore, the conversation-focused design paved the way for more integrated messaging experiences across platforms.
In short, Android 11’s legacy continues through ongoing enhancements in both functionality and user engagement within the Android ecosystem.
Example 9: Android 12
Android 12, released in October 2025, introduced numerous enhancements aimed at user customization and experience. Its design overhaul emphasized personalization while integrating improved privacy features. This version significantly refined the overall aesthetic and functionality of the Android operating system.
Key Features
- Material You: Android 12’s most notable feature is Material You, allowing users to personalize their devices with dynamic color themes based on wallpaper selection.
- Privacy Dashboard: A new Privacy Dashboard provides users with a clear overview of how apps access sensitive data over time.
- Improved Notifications: Notifications received a visual upgrade, making them more intuitive and easier to manage.
- Quick Settings Changes: Enhanced Quick Settings make it simpler to adjust settings like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth with just a swipe down.
- Mic and Camera Indicators: Visual indicators now alert users when an app accesses the microphone or camera, improving transparency.
Legacy Impact
Android 12 set new standards for user privacy and customization. The introduction of Material You sparked interest in personalized themes across devices. Furthermore, its emphasis on data protection influenced future updates by reinforcing Google’s commitment to security. As manufacturers adopt these features, you’ll see a lasting impact on how Android evolves in response to user needs and preferences.
Example 10: Android 13
Android 13, released in August 2025, brought several enhancements focused on user experience and personalization. This version continues the tradition of improving functionality while maintaining compatibility with a broad range of devices.
Key Features
Key features of Android 13 include:
- Themed App Icons: Users can apply color themes to app icons for a more cohesive look across devices.
- Improved Privacy Controls: Enhanced permissions management enables users to control which apps access sensitive data.
- Multi-Language Support: Users can set different languages for individual apps, catering to multilingual households.
- Enhanced Security Updates: Android 13 offers quicker security patches without requiring full system updates.
- Spatial Audio Support: Provides an immersive listening experience through compatible headphones.
Legacy Impact
The legacy impact of Android 13 is significant: It sets new standards in privacy and customization that future versions will likely build upon. By prioritizing user preferences, this version influences how developers approach app design and functionality. Additionally, its focus on aesthetics with themed icons may lead to broader adoption of personalized interfaces across various platforms.